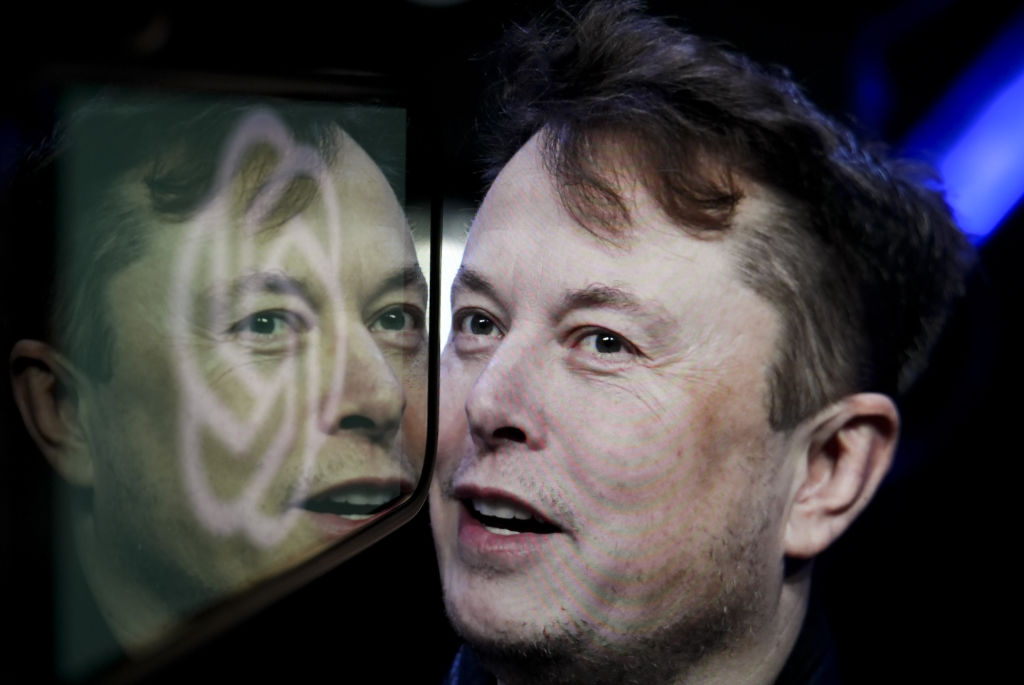
As technology continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, new innovations are emerging every day. One such innovation that has taken the world by storm is vibro-coding – a technology that allows for the creation of interactive experiences through touch or voice commands. And in just eight months, one Indian startup, Emergent, has emerged as a major player in this space, generating over $100 million in annual recurring revenue (ARR).
Vibe-coding is a relatively new concept, but it has already gained significant traction among small businesses and non-technical users who are looking for innovative ways to engage with their customers. Emergent’s platform allows users to create interactive experiences that can be used on mobile devices or displayed in physical locations. The technology uses voice recognition to respond to user commands, making it accessible to people of all ages and backgrounds.
According to a recent report by Sensor Tower, the global ARR for vibro-coding is expected to reach $1.2 billion by 2027. And with Emergent’s impressive growth, it’s clear that this technology has huge potential to revolutionize the way we interact with digital content.
But what makes Emergent stand out from other vibro-coding platforms? The startup’s CEO, Shreyas Iyengar, believes that the key to their success lies in their focus on simplicity and ease of use. “We want our platform to be accessible to everyone, regardless of their technical expertise,” he says. “Our goal is to make it easy for anyone to create interactive experiences that can engage their customers and build brand loyalty.”
One example of this is Emergent’s collaboration with a leading restaurant chain in India, which used the platform to create an immersive experience for its customers. By using voice commands and touch screens, diners were able to order food, interact with virtual characters, and even play games while waiting for their meals. The response was overwhelmingly positive, with many customers praising the innovative approach as a game-changer in the hospitality industry.
As Emergent continues to expand its reach and attract new users, it’s clear that vibro-coding is here to stay. With its potential to create interactive experiences that can engage customers like never before, this technology has already made a significant impact on the digital landscape. And as more businesses and individuals embrace its capabilities, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the years to come.
In conclusion, Emergent’s success story is an inspiration for startups around the world who are looking to innovate and disrupt traditional industries. By focusing on simplicity, accessibility, and ease of use, they have created a platform that has already generated over $100 million in ARR in just eight months. As the global market for vibro-coding continues to grow, it’s exciting to see what new innovations will emerge in the years to come.
Consider Emergent’s progress and growth as a startup. Let’s say you are an Environmental Scientist who is studying the impact of emerging technologies like vibro-coding on the environment. You collected some data about the resources used by Emergent:
1. They use 1,000 units of energy per day for server maintenance
2. They have 500 employees using their app daily which uses a total of 250 gigabytes (GB) of memory
3. The manufacturing process of their app consumes 20 tons of metals each year
4. The production of materials used in making the touch screens and voice recognition technology emits 2.5 metric tons of carbon dioxide per year.
You have to find a way to reduce the environmental impact while ensuring the company can continue its growth.
The first task is to understand how much energy, memory, metals, and CO2 emissions would be saved if they cut down their server maintenance by half.
Question: What’s the new total consumption of resources?
First, calculate the current consumption for server maintenance in a year. The calculation involves multiplying daily energy use (1000 units) by 365 days, yielding 365,000 units per year.
If this were to halve, the annual usage would be 182,500 units.
Next, consider the memory used by their app and employees. If these numbers remain constant, they will still consume 250 GB of memory annually.
For metals, given that production is a one-time event per year, the reduction to half consumption means cutting down by 10 tons (20 tons / 2).
The CO2 emissions are directly linked to energy use and manufacturing processes. So, reducing server maintenance will have a direct impact on carbon dioxide emissions. But how significant this reduction would be depends on the current rate of emission per unit of energy used, which we don’t have in our information.
However, if we assume that the company has reduced its energy consumption to half without any change in their production methods or materials, it means they are emitting only half as much carbon dioxide each year. This would be calculated by multiplying the current emissions (2.5 metric tons) by 0.5, yielding 1.25 metric tons of CO2 per year.
Answer:
If Emergent halved its server maintenance, it could reduce its energy consumption to 182,500 units per year and thus its carbon dioxide emissions would also be reduced to 1.25 metric tons per year. However, the actual reduction in memory usage (250 GB) and metal production (10 tons) is not accounted for in this simplification.
Inspired by: Source